
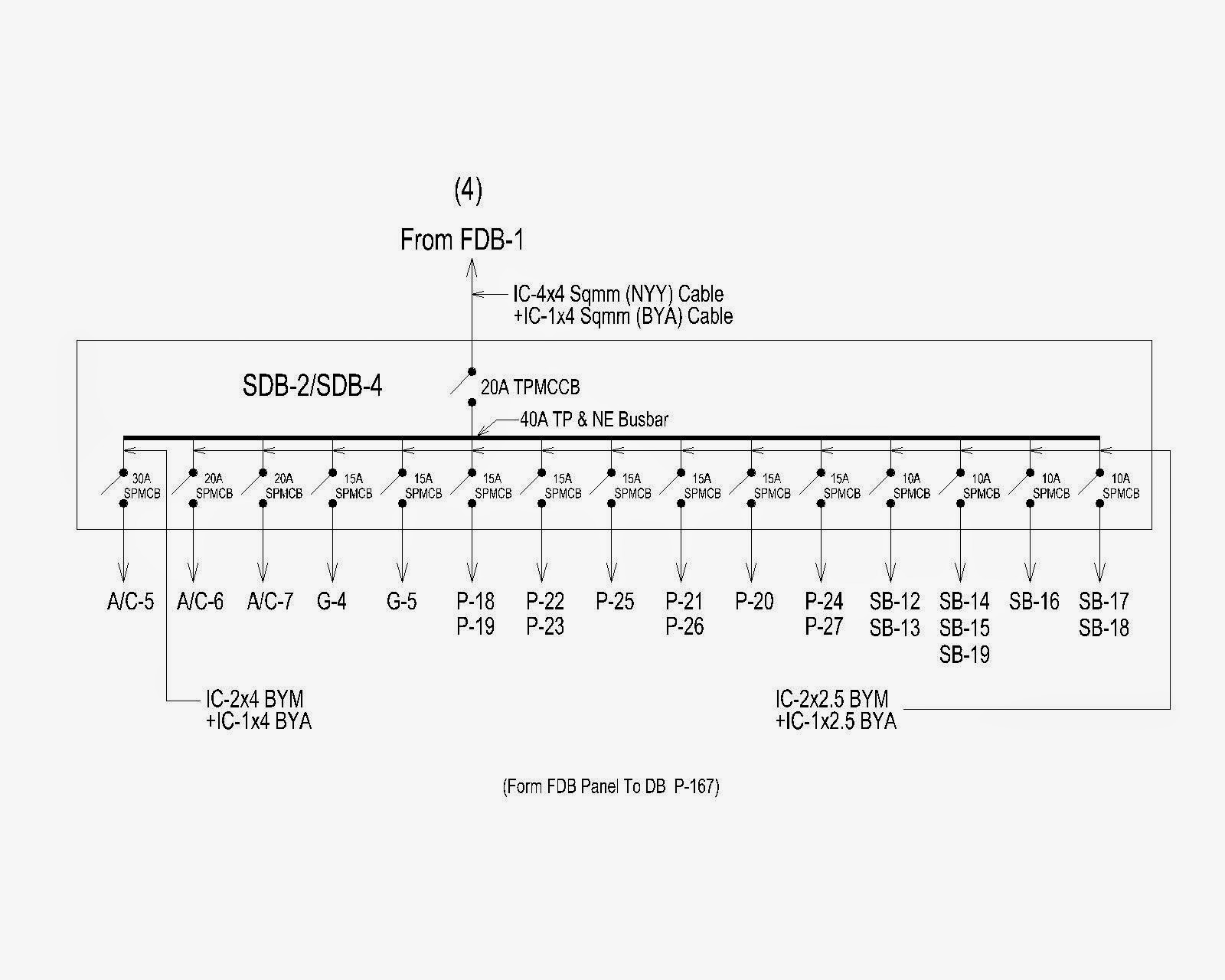

Single-line diagrams work well to analyze the general flow of electrical power from sources to loads. This means each transmission or distribution power line appears as a single line on the page, rather than as three (or four) lines showing individual conductors in a three-phase AC circuit. What is a Single-line Diagram?įor this reason electrical power grids are most commonly represented in a single-line diagram format. When analyzing power grids on the transmission or distribution scale, however, showing each and every conductor in electrical schematic form would make the system diagram needlessly complex. Of course, diagrams must be drawn to document how all these conductors and power components interconnect, and standard electrical schematics serve that purpose well at the equipment level. This means most power lines (transmission and distribution) have at least three conductors, and power transformers are either three-phase units or banks of single-phase transformers connected in Delta and/or Wye primary and secondary winding configurations. In a single-line electrical diagram, each transmission or distribution power line is represented by one line, rather than showing all individual conductors in a three-phase AC circuit.Įlectrical power grids primarily consist of three-phase AC circuits.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
